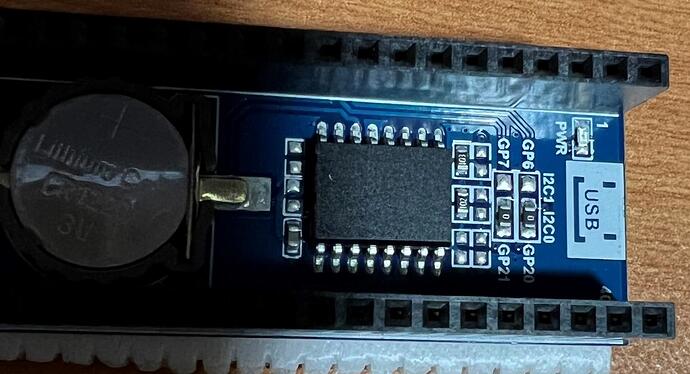
Question 1: Yes. See Pico pin outs.
Pico-R3-A4-Pinout.pdf (377.0 KB)
Question 2: Below is the Python code downloaded from the Waveshare Wiki web page.
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from machine import Pin, I2C
import time
import binascii
# the first version use i2c1
#I2C_PORT = 1
#I2C_SDA = 6
#I2C_SCL = 7
# the new version use i2c0,if it dont work,try to uncomment the line 14 and comment line 17
# it should solder the R3 with 0R resistor if want to use alarm function,please refer to the Sch file on waveshare Pico-RTC-DS3231 wiki
# https://www.waveshare.net/w/upload/0/08/Pico-RTC-DS3231_Sch.pdf
I2C_PORT = 0
I2C_SDA = 20
I2C_SCL = 21
ALARM_PIN = 3
class ds3231(object):
# 13:45:00 Mon 24 May 2021
# the register value is the binary-coded decimal (BCD) format
# sec min hour week day month year
NowTime = b'\x00\x45\x13\x02\x24\x05\x21'
w = ["Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"];
address = 0x68
start_reg = 0x00
alarm1_reg = 0x07
control_reg = 0x0e
status_reg = 0x0f
def __init__(self,i2c_port,i2c_scl,i2c_sda):
self.bus = I2C(i2c_port,scl=Pin(i2c_scl),sda=Pin(i2c_sda))
def set_time(self,new_time):
hour = new_time[0] + new_time[1]
minute = new_time[3] + new_time[4]
second = new_time[6] + new_time[7]
week = "0" + str(self.w.index(new_time.split(",",2)[1])+1)
year = new_time.split(",",2)[2][2] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][3]
month = new_time.split(",",2)[2][5] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][6]
day = new_time.split(",",2)[2][8] + new_time.split(",",2)[2][9]
now_time = binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + week + " " + day + " " + month + " " + year).replace(' ',''))
#print(binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + week + " " + day + " " + month + " " + year).replace(' ','')))
#print(self.NowTime)
self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.start_reg),now_time)
def read_time(self):
t = self.bus.readfrom_mem(int(self.address),int(self.start_reg),7)
a = t[0]&0x7F #second
b = t[1]&0x7F #minute
c = t[2]&0x3F #hour
d = t[3]&0x07 #week
e = t[4]&0x3F #day
f = t[5]&0x1F #month
print("20%x/%02x/%02x %02x:%02x:%02x %s" %(t[6],t[5],t[4],t[2],t[1],t[0],self.w[t[3]-1]))
def set_alarm_time(self,alarm_time):
# init the alarm pin
self.alarm_pin = Pin(ALARM_PIN,Pin.IN,Pin.PULL_UP)
# set alarm irq
self.alarm_pin.irq(lambda pin: print("alarm1 time is up"), Pin.IRQ_FALLING)
# enable the alarm1 reg
self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.control_reg),b'\x05')
# convert to the BCD format
hour = alarm_time[0] + alarm_time[1]
minute = alarm_time[3] + alarm_time[4]
second = alarm_time[6] + alarm_time[7]
date = alarm_time.split(",",2)[2][8] + alarm_time.split(",",2)[2][9]
now_time = binascii.unhexlify((second + " " + minute + " " + hour + " " + date).replace(' ',''))
# write alarm time to alarm1 reg
self.bus.writeto_mem(int(self.address),int(self.alarm1_reg),now_time)
if __name__ == '__main__':
rtc = ds3231(I2C_PORT,I2C_SCL,I2C_SDA)
rtc.set_time('13:45:50,Monday,2021-05-24')
rtc.read_time()
rtc.set_alarm_time('13:45:55,Monday,2021-05-24')
https://www.waveshare.com/wiki/Pico-RTC-DS3231
Select Resources tab, Click Demo Codes to download.
I would use a multimeter to confirm the connections on the board go to the pins they are supposed to and check the battery voltage and connections as @Oliver33 has stated. If thats all ok and the python code does not work then maybe the boards are faulty.
Schematic of board from the Waveshare Web site.
Pico-RTC-DS3231_Sch.pdf (180.2 KB)
Regards
Jim