Well, it has taken me a while, but I’ve got the Pi Zero 2 W + Camera 3 working as a CCTV camera.
The goal was to get the camera streaming RTSP to my Synology Surveillance Station.
Requirements:
-
Pi Zero 2 W
-
OS 32 bit
-
Camera 3 module
-
MediaMTX
-
rpicam-apps
Install:
1. Install the OS 32 bit and update.
2. Set up your network connection and set the localisation settings.
3. Download and install the correct version of MediaMTX for your Pi Zero.
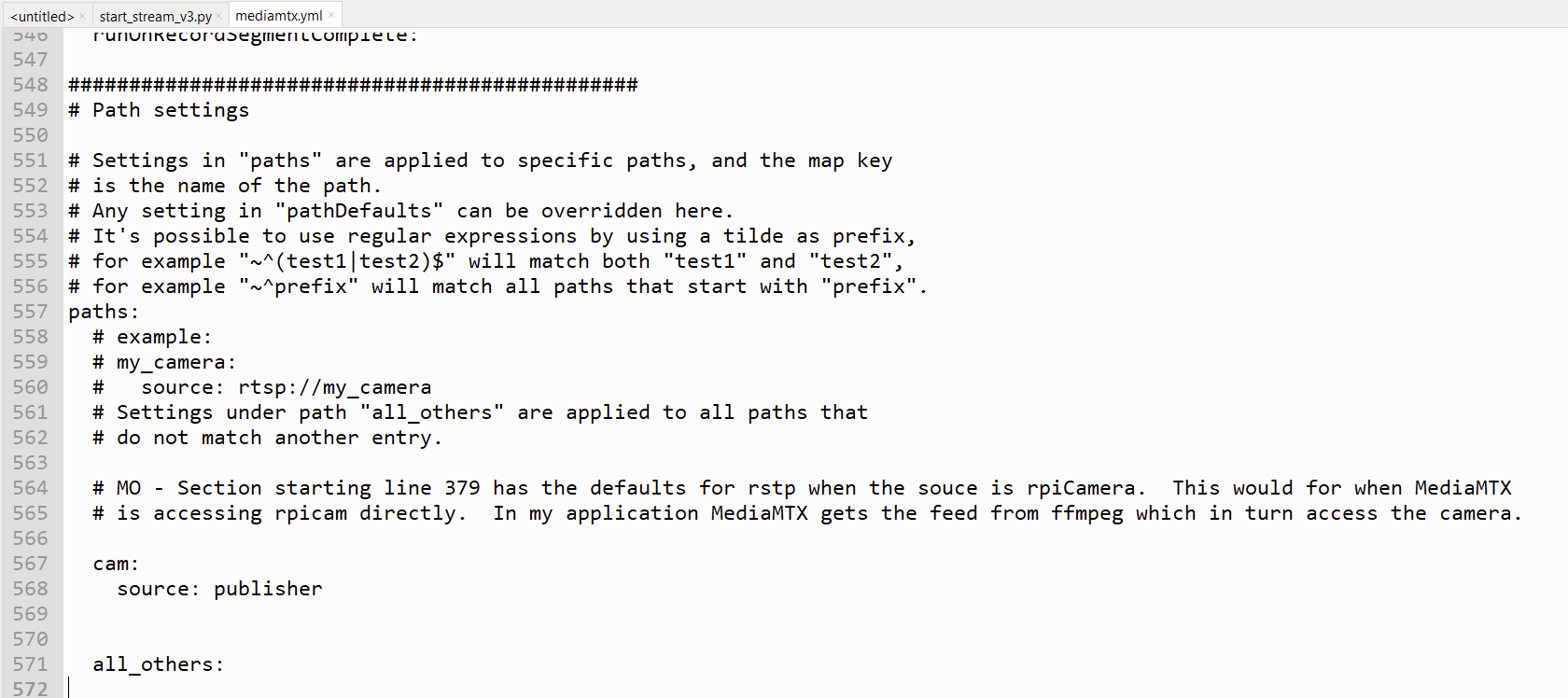
4. Edit mediamtx.yml file located in the folder /home/username/ so that all of the protocols are disabled other than RTSP. Then edit the path at the bottom of the file as per below.
5. Confirm rpicam-apps is installed with “which rpicam-vid” in Terminal. It should be there as part of the OS install.
6. Save the Python code V3 below as /home/username/start_stream.py. Edit the camera name in the drawtext line.
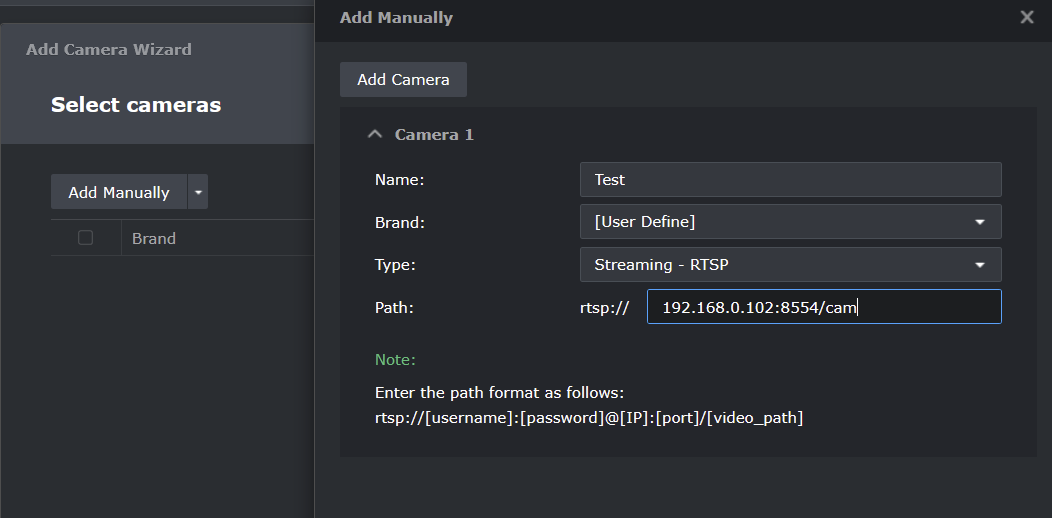
7. In Synology SS go to IP Camera > Add > Add Camera and add your camera as per the snip below.
Tuning:
A clarification first; this is a CCTV camera, not a video camera so resolution is the important thing (so one can identify intruders, read rego etc), not smooth motion. A few FPS is all that’s required.
Tuning is done in the rpicam section stream_start.py.
The V3 code runs fine as 1080p with a frame rate of 4, and better at 2. An FPS rate > 4 gets the CPU load >50% and more importantly, the temperature into the mid 60°s. I found CPU load and temperature higher than this degraded the performance (mainly frame rate) and as the temperature approaches 80°, the Zero lags then stop, losing the stream.
Cutting back the resolution to 720p allows for a faster FPS but with a loss of clarity.
Preview is disabled (for CPU load) and auto-focus set to auto.
On the Zero I ran one Terminal window checking temperature as required, another for start_stream.py and the Task manager showing the CPU load.
Time stamping:
V3 of the code below includes the camera name but no time stamping.
V6 below includes both but this time stamping seems to add significant load to the CPU and so generates more heat, which means running lower resolution and FPS. No doubt more efficient and elegant coding would improve performance but V3 seems a reasonable trade-off for a home CCTV system.
If you do improve my V6 please let me know!
start_stream.py V3
# v1 - First working reliable setup. 1080p with no time stamp
# v2 - Sets autofocus-mode to auto
# v3 - Adds text overlay in ffmpeg
import subprocess
import time
# Start MediaMTX (adjust the path if needed)
mediamtx_proc = subprocess.Popen(
["/usr/local/bin/mediamtx", "/home/morchard/mediamtx.yml"]
)
# Short delay to allow MediaMTX to bind the RTSP port
time.sleep(2)
# Start the rpicam stream piped into FFmpeg with corrected flags
rpicam_cmd = [
"rpicam-vid",
"-t", "0",
"--inline",
"--width", "1920",
"--height", "1080",
"--framerate", "30",
"--nopreview",
"--autofocus-mode", "auto",
"-o", "-"
]
ffmpeg_cmd = [
"ffmpeg",
"-fflags", "+genpts",
"-analyzeduration", "10000000",
"-probesize", "5000000",
"-re",
"-f", "h264",
"-i", "-",
"-vf", "drawtext=fontfile=/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans-Bold.ttf:text='Pi ZeroW2 Cam':fontcolor=white:fontsize=24:box=1:boxcolor=black@0.5:boxborderw=5:x=1500:y=10",
"-c:v", "libx264",
"-preset", "ultrafast",
"-f", "rtsp",
"rtsp://localhost:8554/cam"
]
# Launch rpicam-vid piped into ffmpeg
rpicam_proc = subprocess.Popen(rpicam_cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
ffmpeg_proc = subprocess.Popen(ffmpeg_cmd, stdin=rpicam_proc.stdout)
# Wait for subprocesses to exit (optional - or handle cleanup/signals)
ffmpeg_proc.wait()
rpicam_proc.wait()
mediamtx_proc.terminate()
MediaMTX.yml
Synology SS
start_stream.py V6
# v1 - First working reliable setup. 1080p with no time stamp
# v2 - Sets autofocus-mode to auto
# v3 - Adds camera name text overlay in ffmpeg
# v4 - Adds time stamp overlay via update_timestamp() every 10s.
# v5 - Adds "fps=1," to ffmpeg's -vf to slow the drawtext accessing the txt file to 1 second. Changes update_timestamp() to 60s update.
# v6 - Mods update_timestamp() so instead of writing directly to timestamp.txt, it writes to timestamp.tmp and then rename it.
# Renaming is an atomic operation on most filesystems, so FFmpeg never sees partial content. Changes update_timestamp() to 1s update.
import subprocess
import threading
import time
import signal
import os
# Update overlay text file continuously at the time interval set by time.sleep.
def update_timestamp():
while True:
with open("timestamp.tmp", "w") as f:
f.write(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"))
os.replace("timestamp.tmp", "timestamp.txt")
time.sleep(1)
# Start MediaMTX
mediamtx_proc = subprocess.Popen([
"/usr/local/bin/mediamtx",
"/home/morchard/mediamtx.yml"
])
# Short delay to allow MediaMTX to bind the RTSP port
time.sleep(2)
# Start overlay updater thread.
# Creates and launches a lightweight background thread that runs the update_timestamp() function independently of the main process.
# update_timestamp() is called once.
threading.Thread(target=update_timestamp, daemon=True).start()
# Prepare the camera stream (raw H.264)
rpicam_cmd = [
"rpicam-vid",
"-t", "0",
"--inline",
"--width", "1920",
"--height", "1080",
"--framerate", "30",
"--nopreview",
"--autofocus-mode", "auto",
"-o", "-"
]
# FFmpeg pipeline with drawtext and timestamp from file
ffmpeg_cmd = [
"ffmpeg",
"-fflags", "+genpts",
"-analyzeduration", "10000000",
"-probesize", "5000000",
"-re",
"-f", "h264",
"-i", "-",
"-vf", (
"drawtext=fontfile=/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans-Bold.ttf:"
"text='Pi ZeroW2 Cam':fontcolor=white:fontsize=36:box=1:boxcolor=black@0.5:"
"boxborderw=5:x=w-tw-1500:y=10,"
"fps=1,"
"drawtext=fontfile=/usr/share/fonts/truetype/dejavu/DejaVuSans-Bold.ttf:"
"textfile='timestamp.txt':reload=1:fontcolor=white:fontsize=36:"
"box=1:boxcolor=black@0.5:boxborderw=5:x=w-tw-1500:y=60"
),
"-c:v", "libx264",
"-preset", "ultrafast",
"-f", "rtsp",
"rtsp://localhost:8554/cam"
]
# Launch rpicam and FFmpeg
rpicam_proc = subprocess.Popen(rpicam_cmd, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
ffmpeg_proc = subprocess.Popen(ffmpeg_cmd, stdin=rpicam_proc.stdout)
# Graceful shutdown on Ctrl+C
try:
ffmpeg_proc.wait()
rpicam_proc.wait()
finally:
mediamtx_proc.terminate()
rpicam_proc.terminate()
ffmpeg_proc.terminate()
if os.path.exists("timestamp.txt"):
os.remove("timestamp.txt")